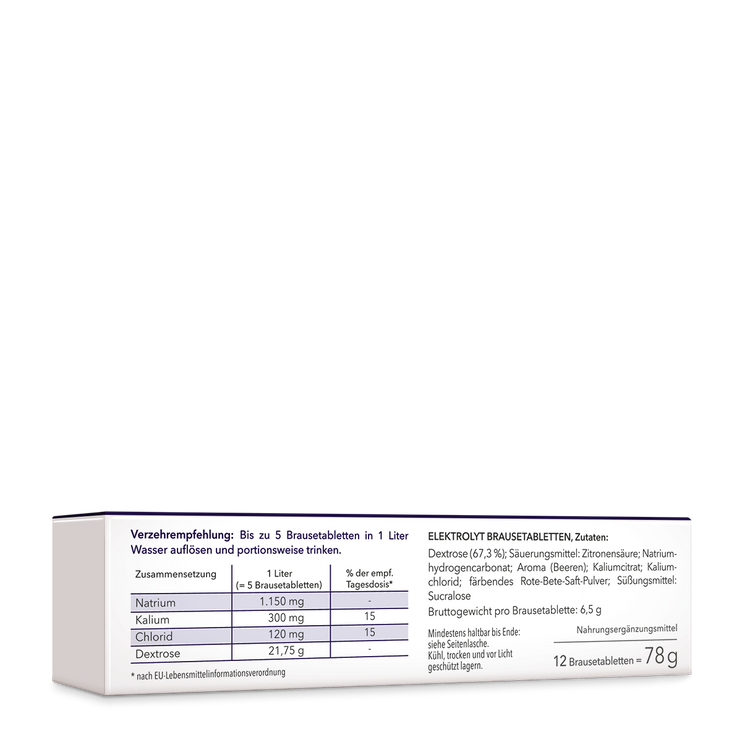
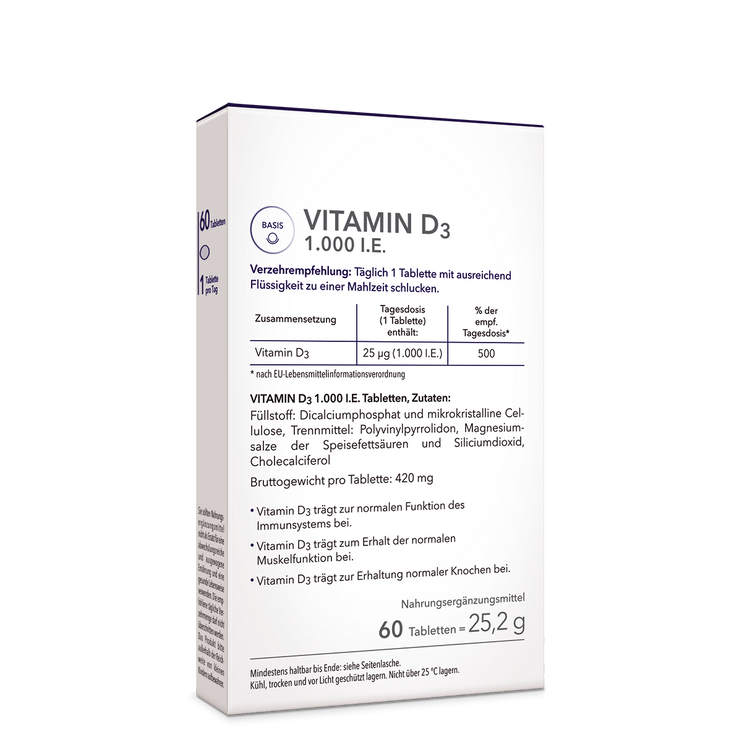
Fit through sport and vital substances
It has never been so easy to eat healthily, exercise and, with the help of individual preventive measures, create the conditions fora long and healthy lifeto accomplish.Exercise and a balanced diet belong together because one supports the other.
Regular fitness training or competitive sports makes you happier and more balancedYou feel good in your body and are also more creative and productive.Studies show that sport and exercise boost moodWith Medicom at your side, you can achieve a lot, including your fitness goals. We support you in your plan with theoptimal supply of vital substances for a fit life.